Abstract
In this chapter, we will introduce the last application of the book, i.e., interbasin transfer. In this process, there are two main components: donor and receiver basins. The purpose of interbasin transfer to redistribute water from a water-rich region to the region with water shortage. The interbasin transfer may help reducing the impact of dry conditions in the region with water shortage.
17.1 Case-Study Site and Dataset
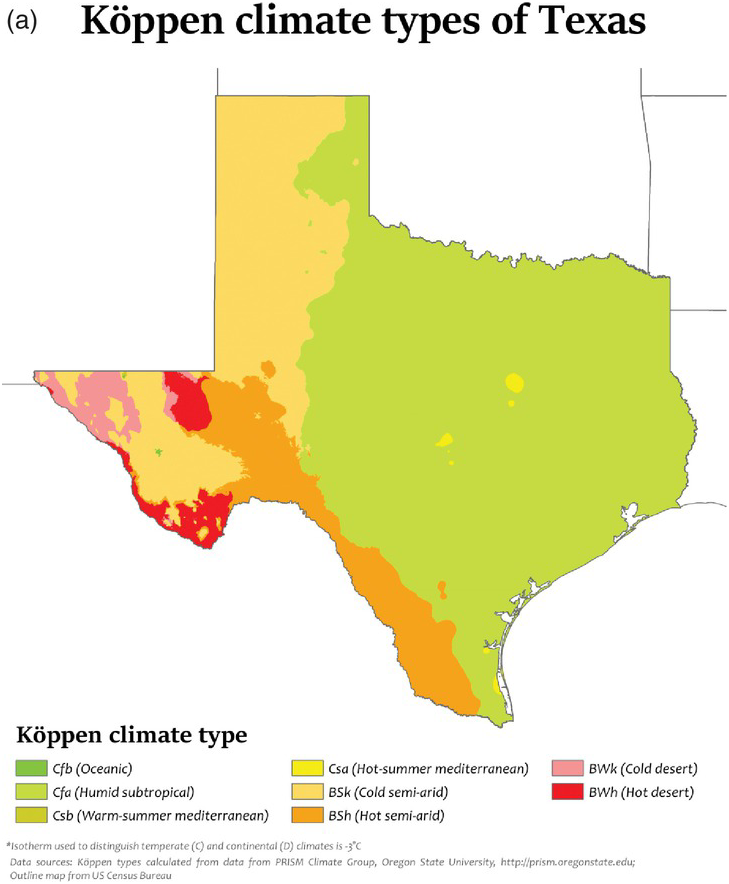
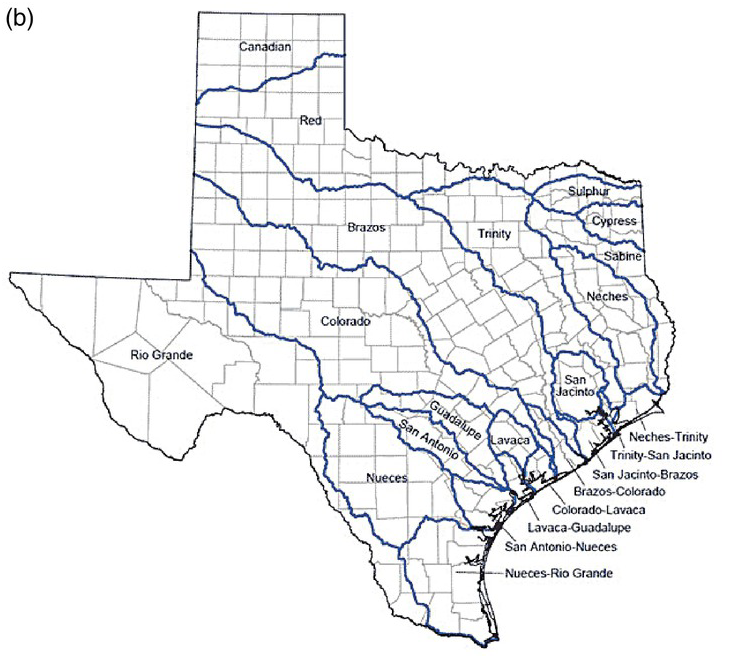
In this chapter, we will provide a synthetic analysis for interbasin transfer using the river systems in Texas, the United States, as an example. Based on the description of Texas, the climate in Texas varies from arid in the west to humid in the east (as shown in Figure 17.1). The major river systems as well as major cities are shown in Figure 17.1. Among all the major river systems, the Brazos, Sabine, and Trinity Rivers carry the largest annual runoff of 6,074,000; 5,864,000; and 5,127,000 acre feet, respectively. Climatewise, the eastern coastal region is in the tropic humid climate region with abundant precipitation throughout the year. However, the central and western parts of Texas are within the arid/semi-arid climate region and may not receive enough precipitation. Thus, it is viable to transport the abundant water from the eastern part of Texas to central and western parts of Texas under the conditions of no or minimum negative impact on the highly developed eastern coastal area of Texas. In this case study, we will choose Lake Houston (USGS 08072000) as a donor reservoir, and E. V. Spence Reservoir (USGS 08123950) as a receiver reservoir to evaluate the possibility of interbasin transfer.
Figure 17.1 (a) Köppen climate types of Texas (retrieved from https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Texas_K%C3%B6ppen.svg).
(b) Major rivers and cities in Texas (retrieved from www.twdb.texas.gov/surfacewater/rivers/index.asp, courtesy of Texas Water Development Board).
Lake Houston was constructed in 1953 and is currently serving as the primary source of water supply for the city of Houston. The E. V. Spence Reservoir is located west of Robert Lee, Texas. In the normal years, the E. V. Spence Reservoir may be sufficient to provide the water supply for Robert Lee and surrounding communities in Coke County. However, during the recent drought, the reservoir storage decreased to less than 0.76% of its capacity. As of June 2016, the lake was back up to 10.4% of its capacity (Wikipedia.org). To illustrate the process, monthly storage is applied. The full capacity storage of Lake Houston is 134,313 acre feet. The full capacity storage of the E. V. Spence Reservoir is 135,704 acre feet. Based on the availability of the dataset (USGS), the data from water year of 2000 to 2016 are applied for analysis. In addition, there is one data value missing for Lake Houston (May 2015) and one for E. V. Spence Reservoir (May 2004). The missing value at Lake Houston and E. V. Spence Reservoir is filled based on the recent drought. The missing value at Lake Houston is filled with the average flow of May, while the missing value at E.V. Spence Reservoir is filled with the average flow of May before water year 2010 (i.e., before the 2010–2013 drought in the southern United States and Mexico). The entire dataset is listed in Table 17.1.
Table 17.1. Storage at Lake Houston and E. V. Spence Reservoir (acre feet).
| Year | Month | USGS08072000 | USGS08123950 | Year | Month | USGS0807200 | USGS08123950 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 10 | 100,800 | 83,700 | 2008 | 10 | 141,900 | 59,510 |
| 2000 | 11 | 136,800 | 88,260 | 2008 | 11 | 143,700 | 56,880 |
| 2000 | 12 | 144,200 | 86,270 | 2008 | 12 | 142,600 | 54,680 |
| 2001 | 1 | 147,200 | 84,840 | 2009 | 1 | 140,600 | 52,590 |
| 2001 | 2 | 145,400 | 83,870 | 2009 | 2 | 137,700 | 51,010 |
| 2001 | 3 | 144,600 | 82,740 | 2009 | 3 | 141,600 | 49,320 |
| 2001 | 4 | 144,100 | 80,930 | 2009 | 4 | 145,100 | 46,400 |
| 2001 | 5 | 141,600 | 78,060 | 2009 | 5 | 143,100 | 43,710 |
| 2001 | 6 | 147,400 | 74,020 | 2009 | 6 | 134,300 | 40,920 |
| 2001 | 7 | 143,500 | 69,470 | 2009 | 7 | 134,900 | 37,290 |
| 2001 | 8 | 140,200 | 64,540 | 2009 | 8 | 137,200 | 34,180 |
| 2001 | 9 | 143,500 | 61,800 | 2009 | 9 | 138,600 | 31,080 |
| 2001 | 10 | 140,600 | 58,570 | 2009 | 10 | 144,700 | 28,530 |
| 2001 | 11 | 134,000 | 58,300 | 2009 | 11 | 144,400 | 26,170 |
| 2001 | 12 | 148,300 | 61,510 | 2009 | 12 | 145,700 | 24,840 |
| 2002 | 1 | 145,000 | 59,730 | 2010 | 1 | 143,300 | 23,950 |
| 2002 | 2 | 144,300 | 57,840 | 2010 | 2 | 143,700 | 24,410 |
| 2002 | 3 | 141,800 | 55,190 | 2010 | 3 | 142,600 | 23,900 |
| 2002 | 4 | 143,000 | 53,860 | 2010 | 4 | 140,300 | 22,990 |
| 2002 | 5 | 136,900 | 52,880 | 2010 | 5 | 141,600 | 25,400 |
| 2002 | 6 | 137,300 | 55,000 | 2010 | 6 | 142,700 | 25,100 |
| 2002 | 7 | 142,900 | 54,760 | 2010 | 7 | 143,500 | 24,530 |
| 2002 | 8 | 140,900 | 51,230 | 2010 | 8 | 137,100 | 22,680 |
| 2002 | 9 | 141,200 | 47,390 | 2010 | 9 | 140,600 | 19,950 |
| 2002 | 10 | 146,500 | 45,600 | 2010 | 10 | 132,300 | 20,810 |
| 2002 | 11 | 150,300 | 44,740 | 2010 | 11 | 134,800 | 18,550 |
| 2002 | 12 | 147,500 | 42,940 | 2010 | 12 | 133,100 | 16,360 |
| 2003 | 1 | 145,500 | 41,410 | 2011 | 1 | 142,100 | 14,600 |
| 2003 | 2 | 148,900 | 40,000 | 2011 | 2 | 138,300 | 13,650 |
| 2003 | 3 | 144,900 | 38,420 | 2011 | 3 | 136,300 | 12,060 |
| 2003 | 4 | 143,000 | 35,540 | 2011 | 4 | 130,300 | 10,130 |
| 2003 | 5 | 139,900 | 32,770 | 2011 | 5 | 118,600 | 8,026 |
| 2003 | 6 | 141,500 | 51,950 | 2011 | 6 | 106,600 | 6,104 |
| 2003 | 7 | 144,000 | 57,600 | 2011 | 7 | 99,040 | 4,027 |
| 2003 | 8 | 140,900 | 53,110 | 2011 | 8 | 87,870 | 2,847 |
| 2003 | 9 | 143,900 | 53,040 | 2011 | 9 | 84,700 | 2,500 |
| 2003 | 10 | 144,700 | 51,590 | 2011 | 10 | 96,990 | 2,362 |
| 2003 | 11 | 144,600 | 49,320 | 2011 | 11 | 114,400 | 2,231 |
| 2003 | 12 | 142,000 | 46,790 | 2011 | 12 | 136,500 | 2,194 |
| 2004 | 1 | 146,500 | 44,630 | 2012 | 1 | 141,700 | 2,249 |
| 2004 | 2 | 145,700 | 42,870 | 2012 | 2 | 144,800 | 2,323 |
| 2004 | 3 | 141,000 | 46,050 | 2012 | 3 | 143,800 | 2,320 |
| 2004 | 4 | 141,200 | 49,040 | 2012 | 4 | 139,000 | 2,215 |
| 2004 | 5 | 145,300 | 63,819 | 2012 | 5 | 134,900 | 2,100 |
| 2004 | 6 | 143,900 | 44,640 | 2012 | 6 | 137,300 | 1,839 |
| 2004 | 7 | 140,200 | 42,840 | 2012 | 7 | 143,700 | 1,463 |
| 2004 | 8 | 138,500 | 43,160 | 2012 | 8 | 139,100 | 1,164 |
| 2004 | 9 | 138,100 | 43,590 | 2012 | 9 | 131,800 | 1,111 |
| 2004 | 10 | 123,300 | 39,490 | 2012 | 10 | 135,700 | 28,440 |
| 2004 | 11 | 146,400 | 53,810 | 2012 | 11 | 131,900 | 28,840 |
| 2004 | 12 | 143,700 | 79,410 | 2012 | 12 | 128,600 | 28,480 |
| 2005 | 1 | 144,500 | 78,630 | 2013 | 1 | 138,300 | 27,800 |
| 2005 | 2 | 150,000 | 78,460 | 2013 | 2 | 139,800 | 27,210 |
| 2005 | 3 | 143,500 | 78,490 | 2013 | 3 | 135,400 | 26,000 |
| 2005 | 4 | 141,200 | 76,190 | 2013 | 4 | 139,100 | 24,790 |
| 2005 | 5 | 140,300 | 73,600 | 2013 | 5 | 138,900 | 23,370 |
| 2005 | 6 | 139,600 | 72,450 | 2013 | 6 | 139,800 | 26,680 |
| 2005 | 7 | 141,600 | 68,290 | 2013 | 7 | 134,000 | 28,510 |
| 2005 | 8 | 141,900 | 85,160 | 2013 | 8 | 132,800 | 27,570 |
| 2005 | 9 | 133,800 | 101,900 | 2013 | 9 | 132,300 | 25,770 |
| 2005 | 10 | 138,300 | 99,360 | 2013 | 10 | 141,700 | 24,170 |
| 2005 | 11 | 138,700 | 97,300 | 2013 | 11 | 140,900 | 22,800 |
| 2005 | 12 | 141,700 | 94,870 | 2013 | 12 | 140,200 | 20,990 |
| 2006 | 1 | 140,600 | 92,960 | 2014 | 1 | 139,300 | 19,030 |
| 2006 | 2 | 142,800 | 91,210 | 2014 | 2 | 139,900 | 17,400 |
| 2006 | 3 | 140,700 | 89,790 | 2014 | 3 | 143,300 | 15,550 |
| 2006 | 4 | 140,100 | 88,650 | 2014 | 4 | 138,100 | 13,410 |
| 2006 | 5 | 142,300 | 87,120 | 2014 | 5 | 140,600 | 11,330 |
| 2006 | 6 | 143,200 | 82,880 | 2014 | 6 | 143,500 | 11,790 |
| 2006 | 7 | 142,900 | 77,900 | 2014 | 7 | 141,400 | 10,450 |
| 2006 | 8 | 140,900 | 72,880 | 2014 | 8 | 136,500 | 8,627 |
| 2006 | 9 | 138,700 | 76,020 | 2014 | 9 | 138,300 | 8,025 |
| 2006 | 10 | 146,700 | 73,890 | 2014 | 10 | 140,100 | 14,670 |
| 2006 | 11 | 136,700 | 71,120 | 2014 | 11 | 137,400 | 13,040 |
| 2006 | 12 | 135,400 | 69,300 | 2014 | 12 | 140,700 | 11,760 |
| 2007 | 1 | 140,300 | 68,460 | 2015 | 1 | 143,300 | 10,730 |
| 2007 | 2 | 134,300 | 67,650 | 2015 | 2 | 139,400 | 10,460 |
| 2007 | 3 | 140,400 | 67,200 | 2015 | 3 | 143,800 | 96,50 |
| 2007 | 4 | 141,900 | 70,340 | 2015 | 4 | 143,200 | 11,410 |
| 2007 | 5 | 144,100 | 74,250 | 2015 | 5 | 140,330 | 18,260 |
| 2007 | 6 | 143,300 | 74,490 | 2015 | 6 | 145,500 | 28,370 |
| 2007 | 7 | 138,600 | 72,600 | 2015 | 7 | 141,100 | 38,570 |
| 2007 | 8 | 136,500 | 77,170 | 2015 | 8 | 137,800 | 39,670 |
| 2007 | 9 | 134,300 | 84,430 | 2015 | 9 | 140,100 | 36,760 |
| 2007 | 10 | 134,200 | 80,920 | 2015 | 10 | 134,300 | 37,830 |
| 2007 | 11 | 138,100 | 77,460 | 2015 | 11 | 144,600 | 46,240 |
| 2007 | 12 | 140,400 | 75,980 | 2015 | 12 | 145,400 | 50,110 |
| 2008 | 1 | 140,200 | 74,570 | 2016 | 1 | 144,300 | 50,840 |
| 2008 | 2 | 143,700 | 72,700 | 2016 | 2 | 141,800 | 49,390 |
| 2008 | 3 | 144,100 | 71,540 | 2016 | 3 | 147,400 | 48,020 |
| 2008 | 4 | 141,500 | 70,370 | 2016 | 4 | 151,100 | 48,130 |
| 2008 | 5 | 142,400 | 68,160 | 2016 | 5 | 154,400 | 51,810 |
| 2008 | 6 | 138,200 | 66,990 | 2016 | 6 | 150,100 | 53,790 |
| 2008 | 7 | 135,400 | 65,340 | 2016 | 7 | 142,100 | 53,430 |
| 2008 | 8 | 141,300 | 63,400 | 2016 | 8 | 144,200 | 50,120 |
| 2008 | 9 | 144,000 | 62,440 | 2016 | 9 | 143,100 | 49,630 |